
https://platefulldiet.com/
“High-fiber” foods are those that include a lot of fiber, a special kind of plant-based food that your body cannot break down. Although we cannot digest fiber like we can other nutrients, it is essential for the health of your stomach and body.
Why Is Fiber Important?
Fiber
helps you have regular bowel movements, which helps you avoid constipation.
keeps you from overeating by extending the feeling of fullness in your stomach.
helps control blood sugar levels
lowers dangerous cholesterol, which is good for the heart.
Fiber comes in two main varieties. What It Does: Examples
Soluble fiber slows down digestion by combining with water in your stomach. Oats, apples, beans, and chia seeds
Insoluble fiber increases the amount of your stool and makes it easier for meals to flow through your body. Whole grains, nuts, and carrots
Fruits as Examples of Food Groups Berries, oranges, pears, bananas, and apples
Veggies Kale, spinach, broccoli, and carrots
Whole Grains Whole wheat bread, oats, and brown rice
Legumes and Beans Chickpeas, black beans, and lentils
Seeds and Nuts Sunflower seeds, chia seeds, and almonds
How Much Fiber Do You Need?
Age Range Daily Fiber Objective
Children aged 9 to 13 20–25 grams
Teens (ages 14–18) 25–30 grams
Adults 25–38 grams
FAQ: High-Fiber Foods
Q1: Can I lose weight by eating fiber?
Indeed! Fiber prolongs feelings of fullness, allowing you to consume less without experiencing hunger.
Question 2: Does fiber assist with skin or acne?
Sort of! It aids in body cleansing, which benefits your skin as well.
Q3: Is there fiber in junk food?
No. Soda, chips, and cookies typically have no fiber at all.
Question 4: Can I consume too much fiber?
Bloating or gas may result from eating too much fiber all at once. To assist, drink extra water!
https://www.youtube.com/@Platefulldiet
1. Enhances Digestion
Fiber helps maintain regular bowel movements and gives your stool more volume, which helps keep your gut healthy and helps you avoid constipation.
2. Promotes Heart Health
By lowering LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, soluble fiber can help lessen the risk of heart disease.
3. Regulates Blood Sugar
Fiber helps control blood sugar increases and reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes by slowing the absorption of sugar.
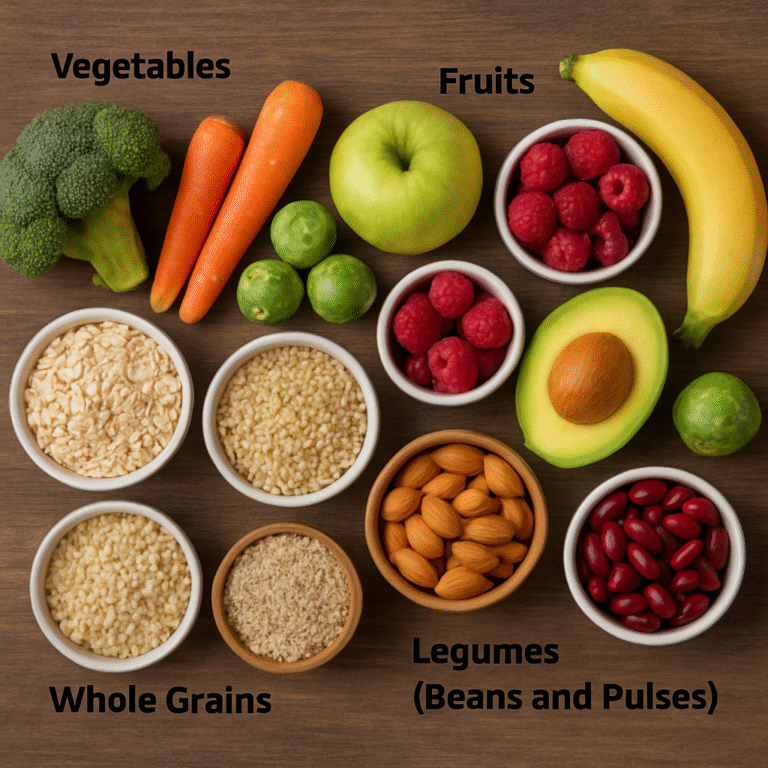
4. Assists with Weight Control
High-fiber foods keep you fuller for longer, reducing unnecessary snacking and supporting healthy weight loss or maintenance.
5. Boosts Gut Health
Fiber feeds the good bacteria in your intestines, improving digestion and overall immunity.
6. Reduces Risk of Certain Diseases
A fiber-rich diet has been linked to lower risks of stroke, hypertension, and some cancers.
What is Dietary Fiber and Why is it Important?
Plant-based foods contain dietary fiber, a kind of carbohydrate that the body is unable to completely digest. Fiber gives your diet bulk and promotes intestinal health since, in contrast to other carbohydrates, it typically survives the digestive process undamaged.
Why is Dietary Fiber Important?
-
Promotes healthy digestion and prevents constipation.
-
Supports heart health by lowering LDL cholesterol.
-
Helps control blood sugar and reduces diabetes risk.
-
Aids in weight management by keeping you full longer.
-
Feeds healthy gut bacteria, improving immunity and nutrient absorption.
High Fiber Food Chart (Printable Table)
High-Fiber Food Chart
This printable chart lists common high-fiber foods along with their average fiber content per serving. Use it as a quick reference to plan a fiber-rich diet.
|
Food |
Serving Size |
Fiber (grams) |
|
Lentils (cooked) |
1 cup |
15.6 |
|
Black Beans (cooked) |
1 cup |
15.0 |
|
Chickpeas (cooked) |
1 cup |
12.5 |
|
Oats (rolled, cooked) |
1 cup |
8.0 |
|
Apple (with skin) |
1 medium |
4.4 |
|
Pear (with skin) |
1 medium |
5.5 |
|
Broccoli (cooked) |
1 cup |
5.1 |
|
Carrots (raw) |
1 cup |
3.6 |
|
Almonds |
1 oz (23 nuts) |
3.5 |
|
Chia Seeds |
2 tbsp |
10.0 |
|
Avocado |
1 medium |
10.0 |
|
Quinoa (cooked) |
1 cup |
5.2 |
Sample High Fiber Meal Plan (1 Day)
Breakfast – ~10g fiber
-
Oatmeal made with rolled oats (1 cup cooked) – 8g fiber
-
Topped with raspberries (½ cup) – 4g fiber
-
Sprinkle chia seeds (1 tbsp) – 5g fiber
-
Drink: Black coffee or green tea
Mid-Morning Snack – ~5g fiber
-
Apple (medium, with skin) – 4.4g fiber
-
10 raw almonds – 1.3g fiber
Lunch – ~9g fiber
-
Quinoa salad with:
-
Quinoa (1 cup cooked) – 5g fiber
-
Chickpeas (½ cup cooked) – 6g fiber
-
Mixed greens, cucumber, tomato – ~2g fiber
-
-
Olive oil & lemon dressing
Afternoon Snack – ~4g fiber
-
Carrot sticks (1 cup raw) – 3.6g fiber
-
Hummus (2 tbsp) – 1g fiber
Dinner – ~8g fiber
-
Baked salmon with roasted broccoli (1 cup cooked) – 5g fiber
-
Sweet potato (1 medium, baked with skin) – 3g fiber
-
Side of mixed leafy greens – ~1g fiber
Total Fiber: ~36–38g
(Daily recommended fiber intake: 25g for women, 38g for men)
